How to Find Your IP Address
Jun 15, 2023 | Share
FAQ, Technology
Internet providers generally assign one public IP address to each customer, and it’s always assigned to the first device connected to the modem or fiber ONT—the router. To share that one connection, your router creates and assigns private IP addresses to all your devices. So, when you open a mobile browser, your data leaves your private IP address and is routed through the public one.
The easiest way to find your public IP address is to google, “What is my IP address?” If you’re looking for the private IP address of a specific device, that’s easy too, but the process isn’t the same for every device. We’ll show you how to find these addresses on mobile devices, computers, and game consoles.
Get your public IP address
You can find your public IP address by running our speed test. The IP address number appears in the results.
Get your public IP address
You can find your public IP address by running our speed test. The IP address number appears in the results.
How to find your public IP address in a browser
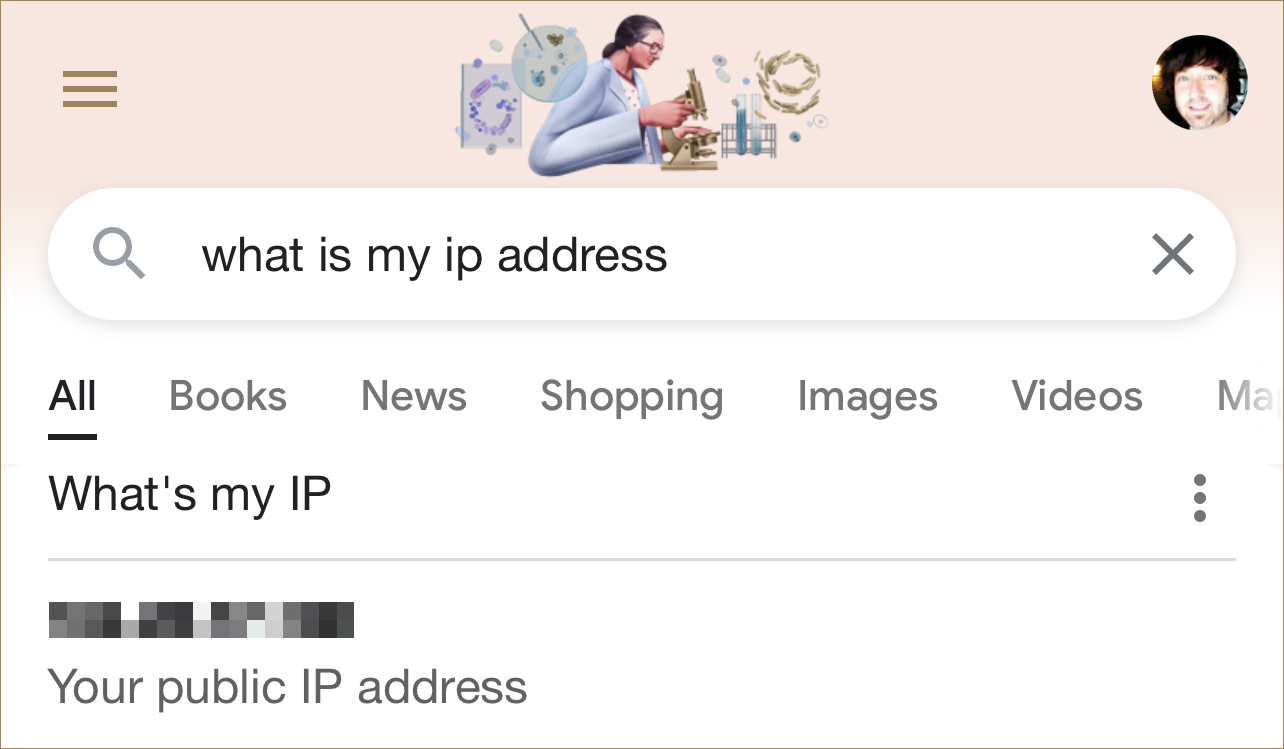
One simple way to find your public IP address is to ask Google. The steps are pretty easy:
Step 1: Open any web browser.
Step 2: Go to google.com.
Step 3: Enter What is my IP address in the search field.
Other websites will list your public IP address along with additional information, such as your rough location and latency.
How to find your private IP address in Android 11 (Google)
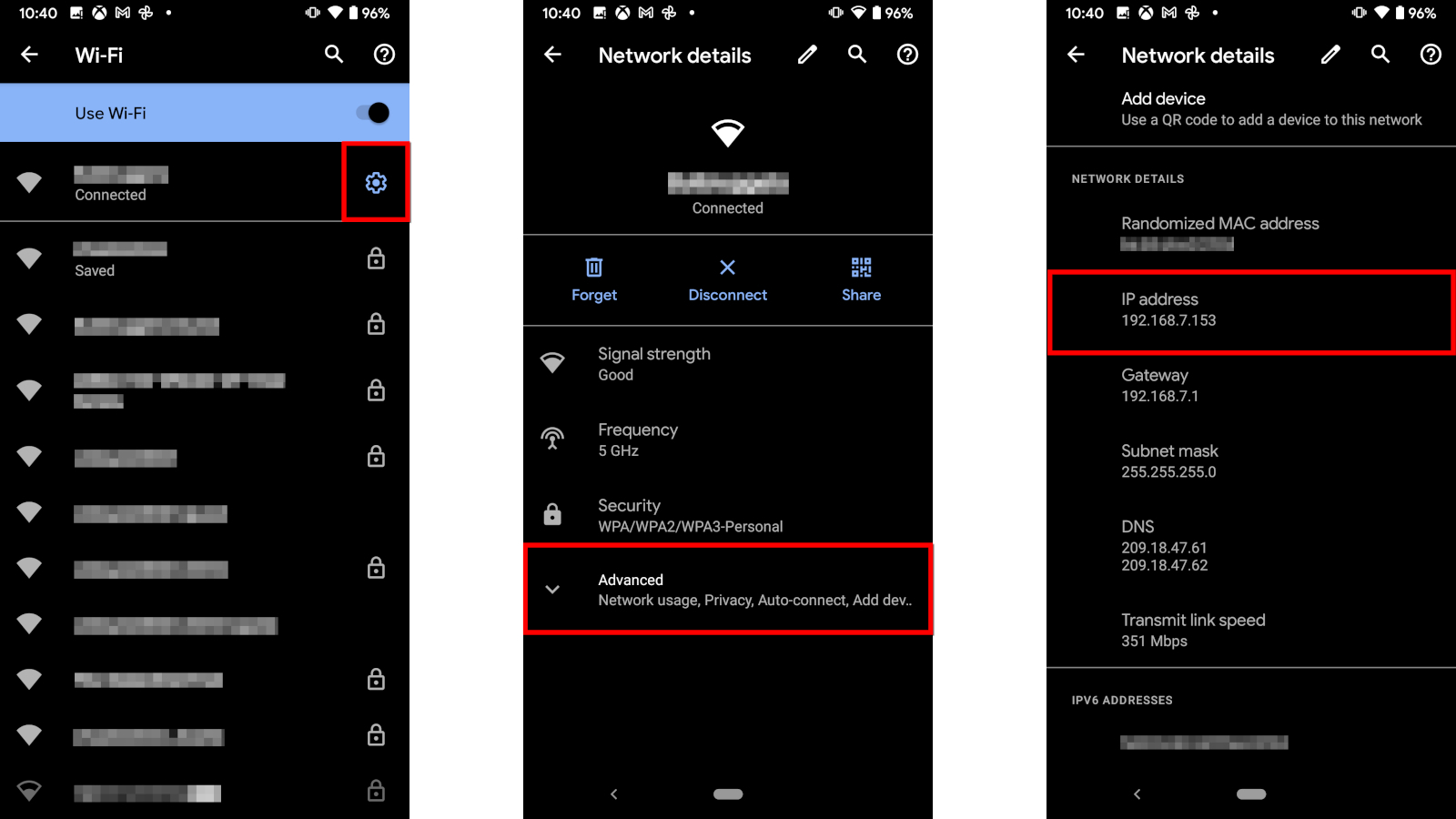
If you have a Samsung device, skip to the next section. Otherwise, the following instructions are for stock Android.
Step 1: Expand the Quick Settings menu from the top and tap on the gear icon.
Step 2: Tap on Wi-Fi.
Step 3: Tap on the gear icon next to your current Wi-Fi connection.
Step 4: Tap Advanced.
The number you want appears under IP Address.
How to find your private IP address in Android 10/11 (Samsung)
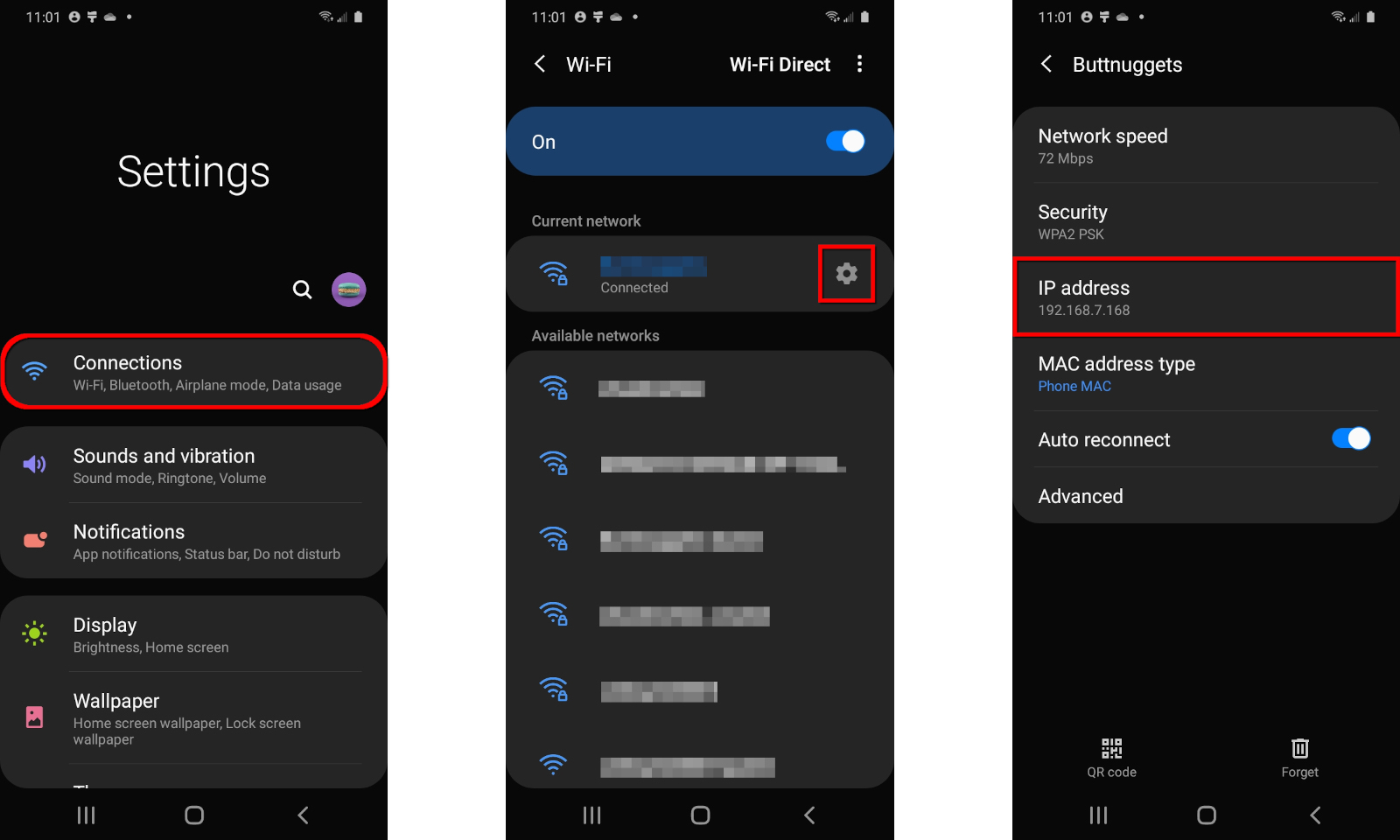
Step 1: Expand the Quick Settings menu from the top and tap on the gear icon.
Step 2: Tap on Connections.
Step 3: Tap on Wi-Fi.
Step 4: Tap on the gear symbol next to your current Wi-Fi connection.
The number you want appears under IP Address.
How to find your private IP address in iOS and iPadOS
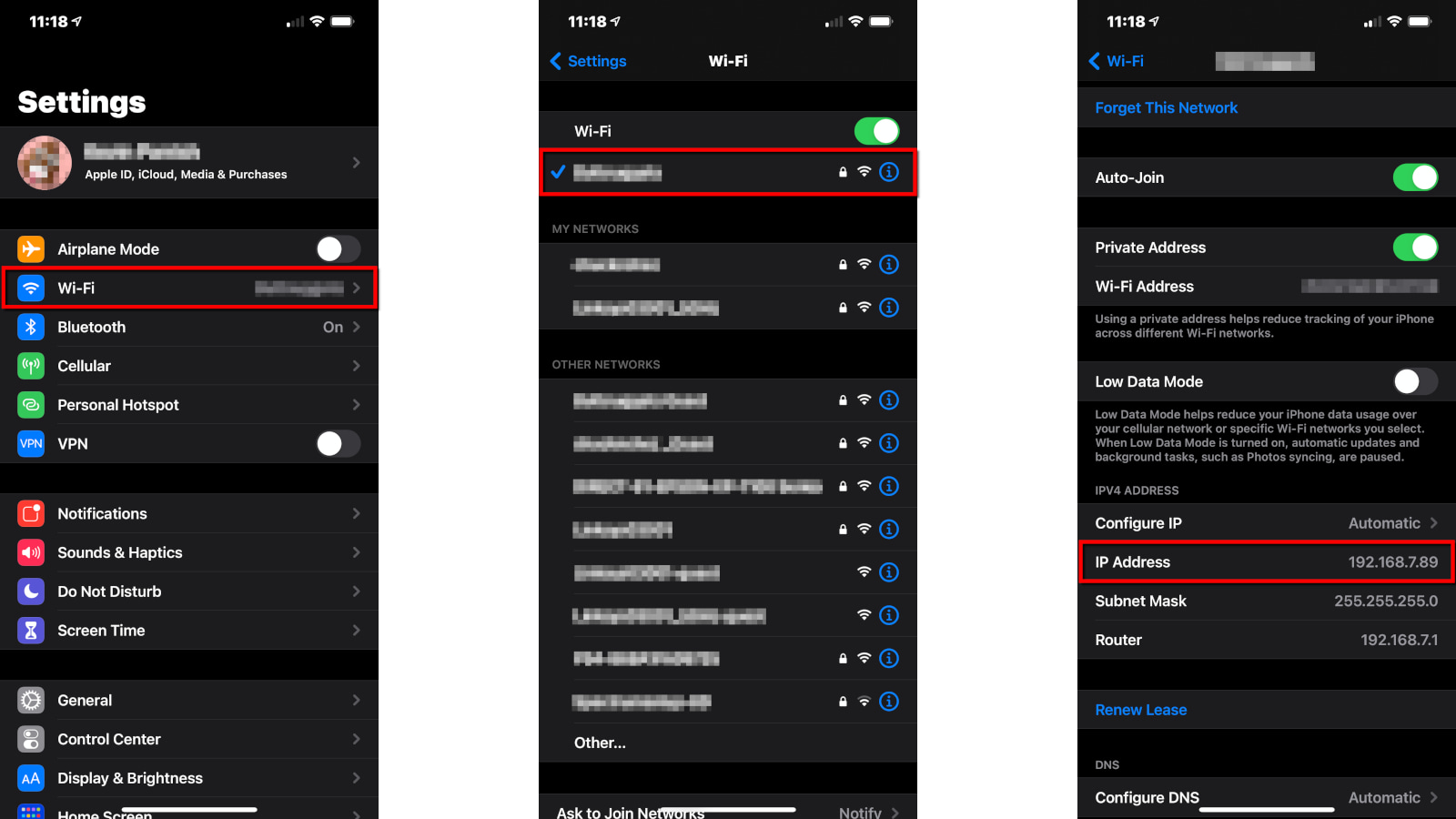
Step 1: Tap to open the Settings app.
Step 2: Tap Wi-Fi.
Step 3: Tap on your current Wi-Fi connection.
The number you want appears next to IP Address.
How to find your private IP address in Windows (10 & 11)
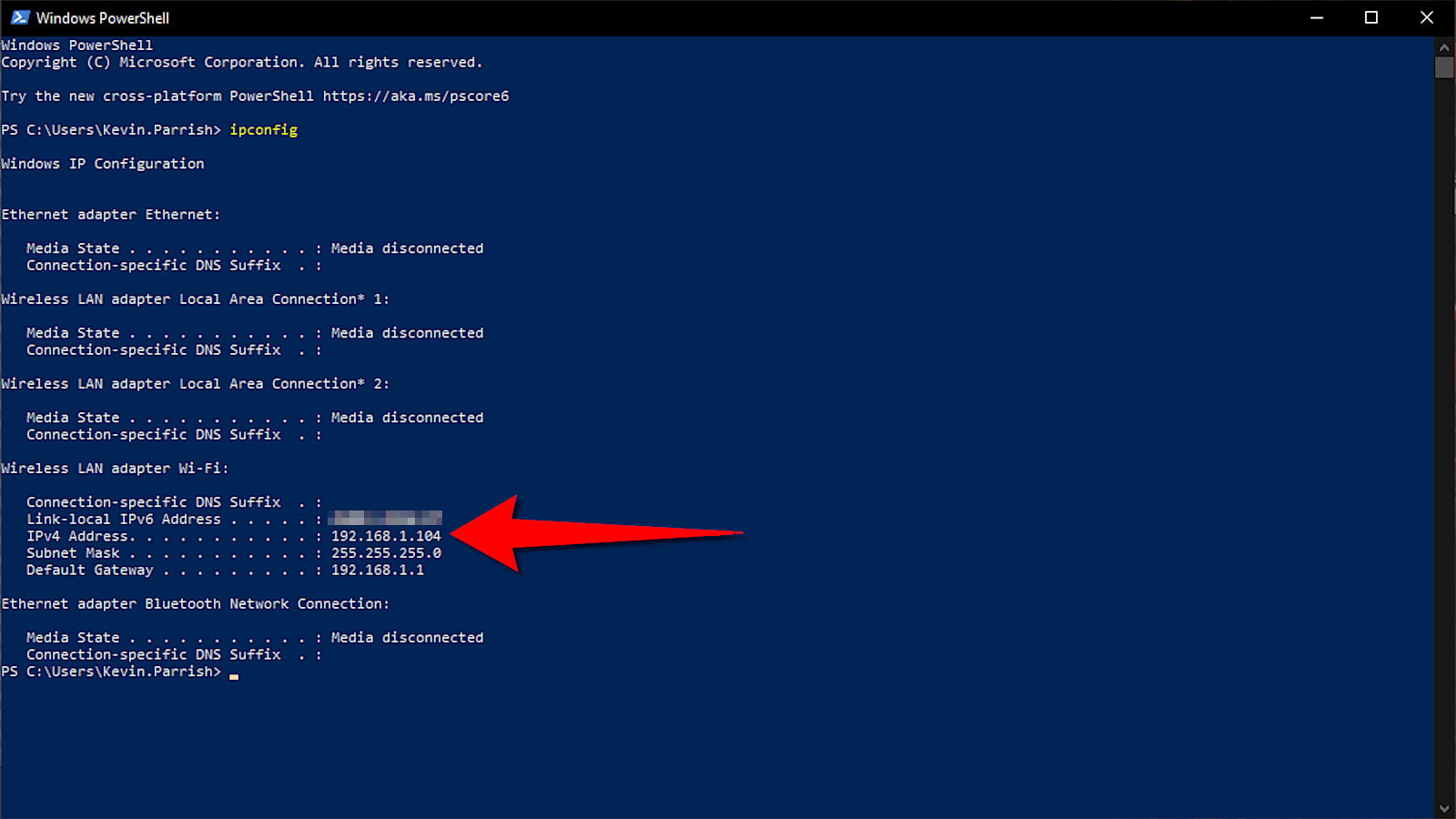
The fastest way to find your private IP address in Windows is to use the IPCONFIG command. To do this, follow these steps:
Step 1: Right-click on the Start button and select Windows Power Shell (Windows 10) or Terminal (Windows 11) on the Power User Menu.
Step 2: Type the command IPCONFIG into the Windows PowerShell or Terminal window and press the Enter key. This will list all the Windows IP configuration information.
The number you need appears next to IPv4 Address, as highlighted above. Also, the number next to Default Gateway is your router’s private IP address (if you’re curious).
How to find your private IP address in macOS
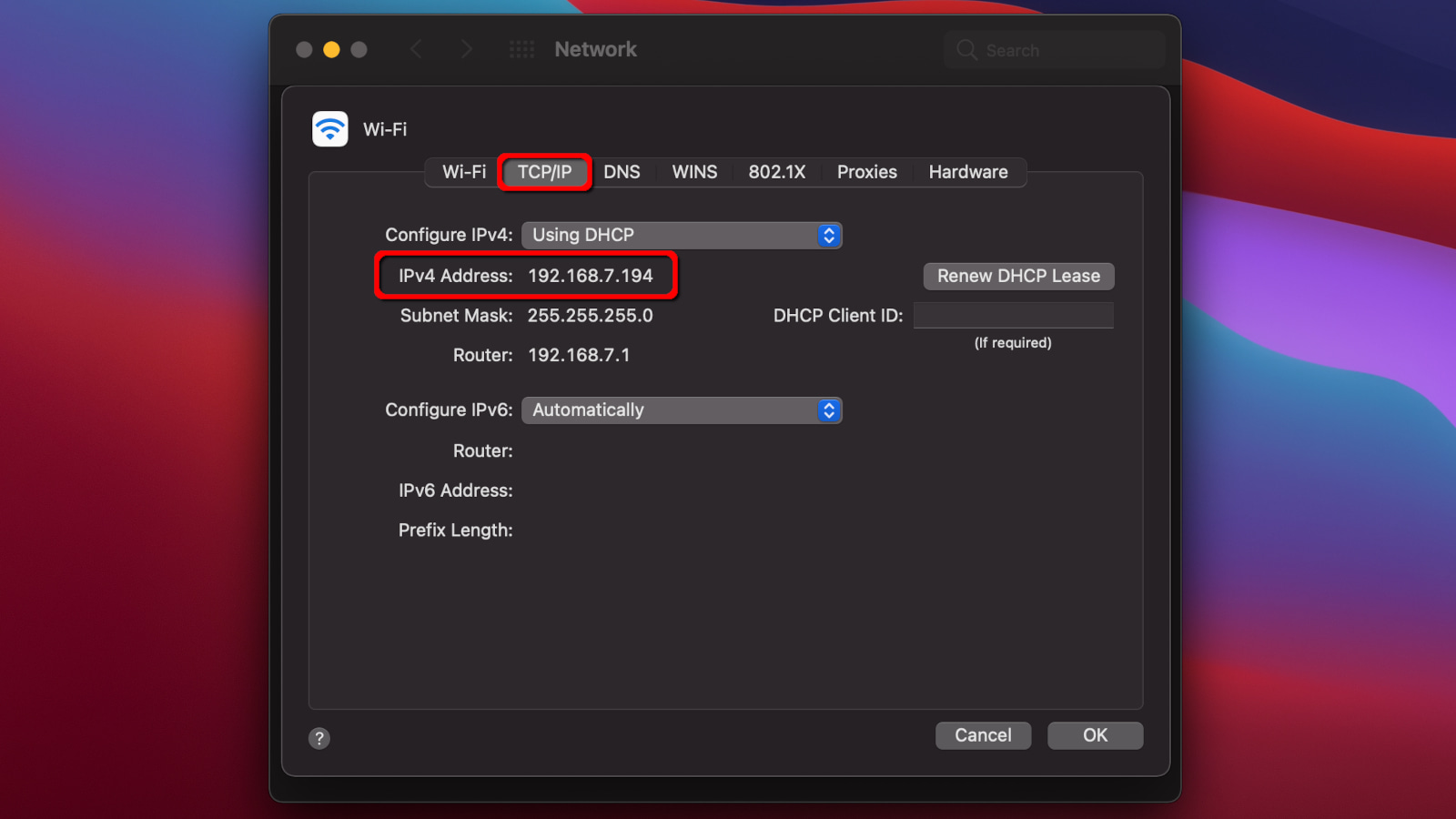
Step 1: Click on the Apple icon, and choose System Preferences. Alternatively, you can click on the System Preferences icon displayed on the Dock (if available).
Step 2: Select Network.
Step 3: Select your network, and then click Advanced at the bottom of the window.
Step 4: Select the TCP/IP tab.
The number you need appears next to IPv4 Address, as shown above.
How to find your private IP address on game consoles
Xbox (One/Series S/Series X)
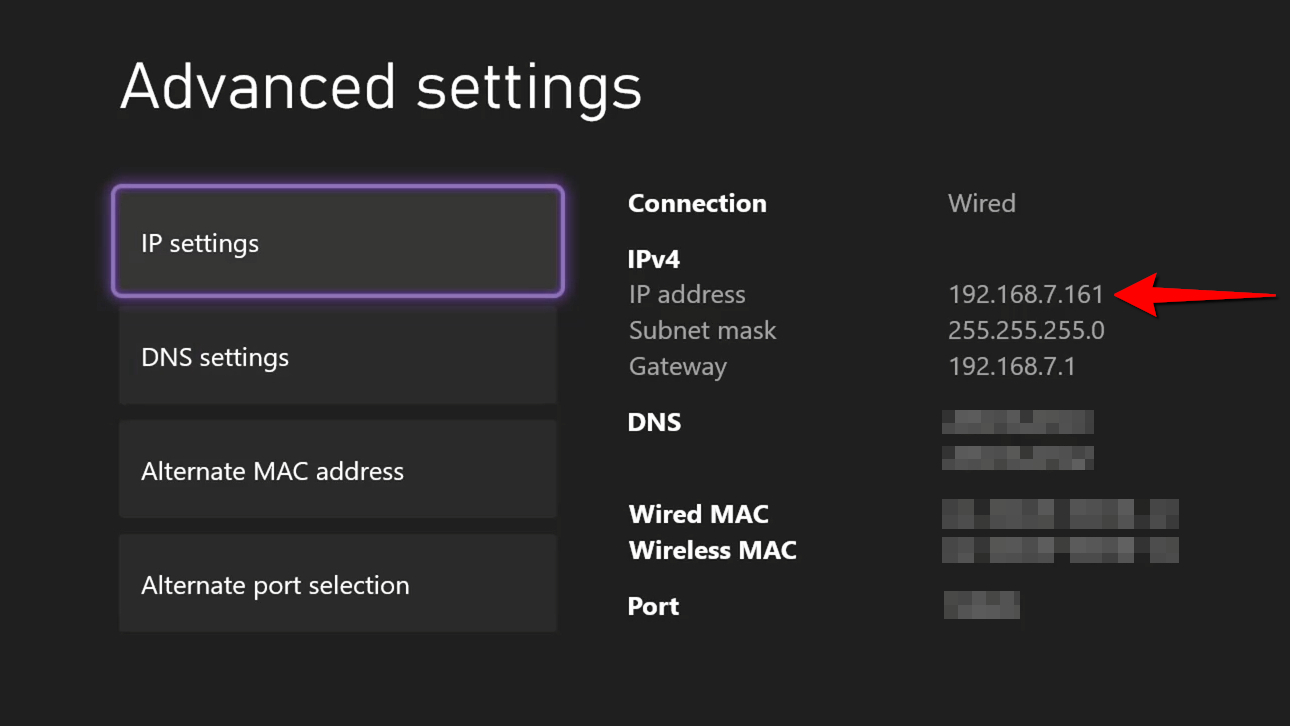
Step 1: Press the Xbox button on your controller to open the guide.
Step 2: Select the Profile & system tab.
Step 3: Select Settings.
Step 4: Select General.
Step 5: Select Network settings.
Step 6: Select Advanced settings.
On the following screen, the IP Settings category is selected by default. The number you want appears on the right next to IP Address.
PlayStation 5
Step 1: Navigate to Settings using the cog wheel in the top-right of the home screen.
Step 2: Select Network.
Step 3: Select View Connection Status.
Step 4: Scroll down and view your IP address next to the label IPv4 address.
PlayStation 4
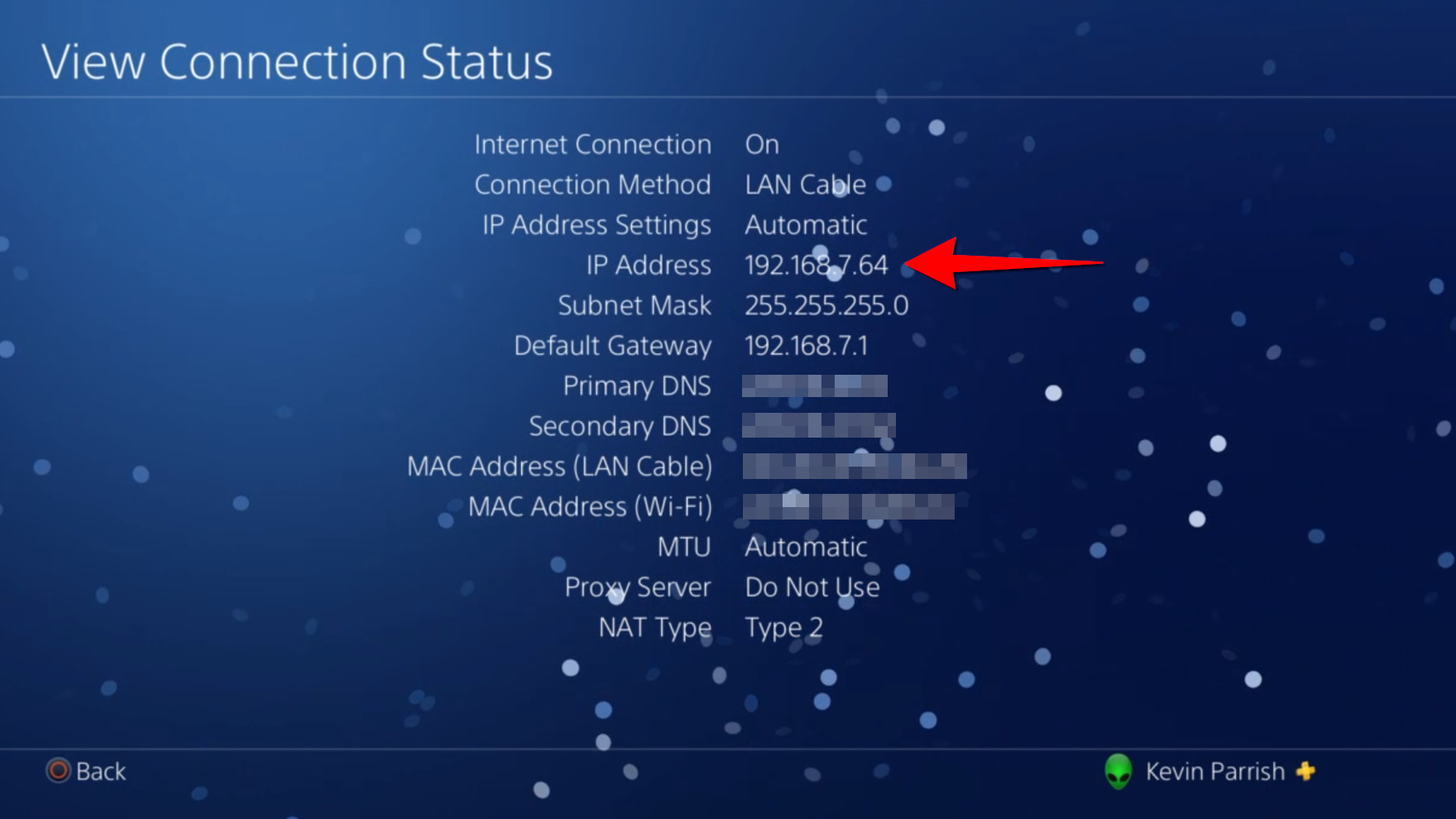
Step 1: Select Settings on the menu.
Step 2: Scroll down and select Network.
Step 3: Select View Connection Status.
The number you want appears next to IP Address.
Nintendo Switch
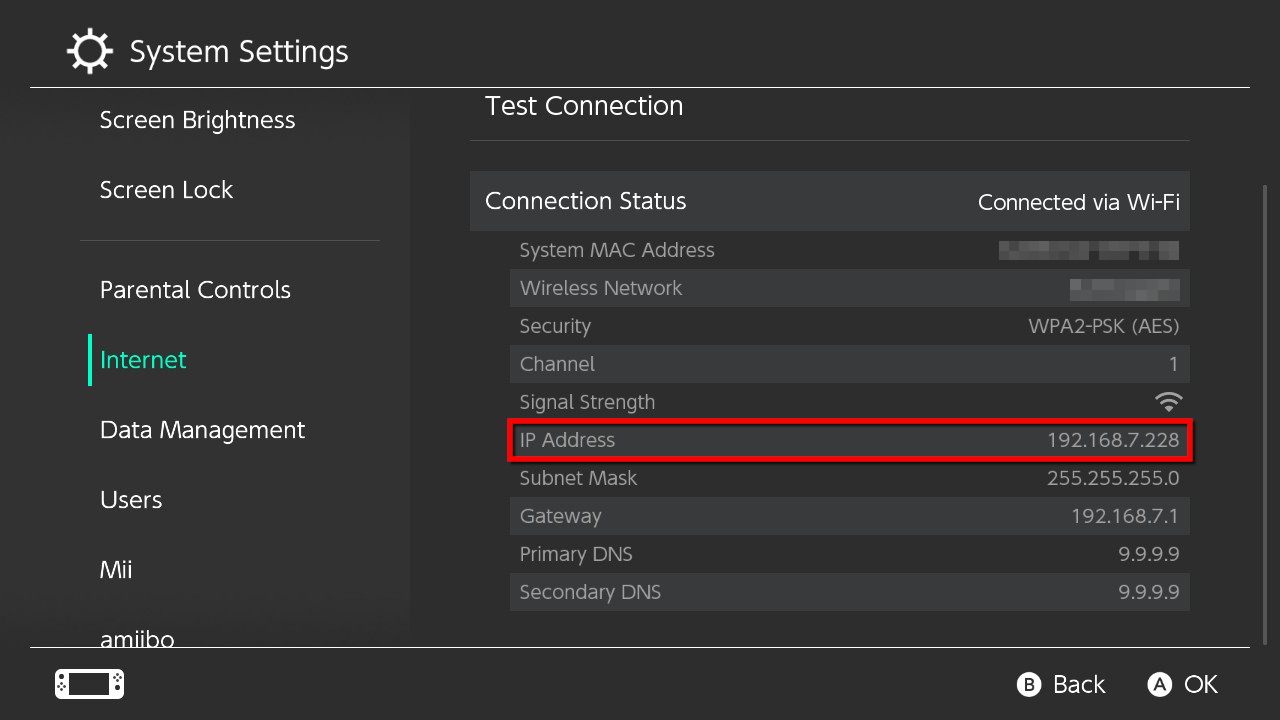
Step 1: Select System Settings on the Home screen.
Step 2: Select Internet listed on the left.
The number you want appears next to IP Address under Connection Status.
Pro tip:
Having issues with your internet connection? See what other options are available in your area.
FAQ about IP addresses
What is an IP address?
An IP address is an ID number that identifies your device on a local and a global network.
The term IP is short for internet protocol, which are the rules and standards that devices use to communicate with each other over all connected networks. This protocol is responsible for making sure that all requests—like a website query and a server’s response—go where they need to go.
Why do I need an IP address?
You need an IP address to send and receive data from remote servers without the need for a direct, physical connection.
All devices have a physical address—their MAC address—that is used only to transfer data between two devices connected to the same local network. To send and receive data from a computer located outside your local network—the internet in this case—you need an IP address assigned to your device’s physical address.
For example, imagine that your street is your local network, all the homes are devices, and all the driveways are their connections. You can walk next door and hand deliver a flyer to your neighbor—it’s an exchange between two local devices. But you can also use a mailbox to send the same flyer to your neighbor or to someone else in a completely different neighborhood.
What’s the difference between a public IP address and a private IP address?
A public IP address is used when your home network communicates with anything outside your home’s local network. Your ISP assigns a single public IP address to you, and all your devices use that same public IP address when communicating with the internet.
A private IP address is the unique ID your router assigns to the different devices on your home network. Every device has its own private IP address that it uses to communicate within your home network.
So, to sum it up, when you run a google search on your computer, your computer talks to your router via its private IP address, and your router talks to the internet via your network’s public IP address.
How do I get an IP address?
You get an IP address from your internet provider or your router, depending on the device. This is where private vs. public IP addresses come into play.
Your internet connection starts at the modem, but it doesn’t have an IP address that the world can see. Instead, your internet provider assigns an IP address to the device physically connected to the modem. In most cases, it’s your wireless router.
The router, in turn, has a private IP address not seen by your internet provider or the internet. It uses this address to assign a unique address to all your wired and wireless devices. So, if your router has a private IP address of 192.168.0.1, then the first connected device is likely 192.168.0.2.
If you have a device that can access your local network using a wired and wireless connection, it has two private IP addresses: one assigned to the Ethernet hardware and one assigned to the Wi-Fi radio. Each of these hardware components has a MAC address the router uses to assign private IP addresses.
As for the public IP address, your internet provider can’t just make up a new number for you. There are large international organizations that divide up available numbers by region. These regional organizations then give them out to ISPs that operate in those regions so that they can assign them to devices—like your router—on their network.
Is my public or private IP address permanent?
No, typically all IP addresses are “dynamic,” meaning they frequently change.
Public IP addresses assigned by internet providers generally last for 14 days. However, the address will change each time you reboot the device connected directly to your modem.
Private IP addresses assigned by your router typically last for 24 hours. Again, this number may change if you reboot the device connected to your router. It will also change if you access a different network, like connecting to Wi-Fi at your local coffee shop.
The only time your IP address doesn’t change is when it’s a “static” number. Internet providers generally assign static IP addresses to enterprise clients as part of a paid business plan. However, you can assign static private IP addresses to your devices through the router if you need to forward specific types of data.
Can I be tracked by my public IP address?
Yes, your internet provider and other third parties can track your public IP address. Private IP addresses generally can’t be tracked due to the way your router masks and handles data.
For example, advertisers can use your public IP address to display customized ads based on your location. Media companies like Netflix can also use that information to restrict access to their content. Your online activity can be tracked too, even if you’re browsing in private or incognito mode.
As we covered earlier, the first two segments in your IP address identify the network. In this case, these two segments reveal not only your provider but also your city and state. The second two segments identify your router, but there’s nothing specific to retrieve from these latter number groups.
Since IP addresses change fairly often, tracing them back to a specific person or home address is rather hard unless someone subpoenas that information. The address does, however, give a fairly good idea of where information is going. For example, one developer was able to create a program that tweeted every time someone from the US congress edited a Wikipedia article.1
If you don’t want your location to be public, you can use a VPN service to hide your IP address. For more information, check out our review of the best VPN services.
What’s the difference between IPV4 addresses and IPV6 addresses?
IPV4 and IPV6 are protocols used to create IP addresses. IPV4, the older of the two, is a 32-bit address scheme capable of creating over 4 billion IP addresses. Amazingly, we’ve used all those up.
IPV6 was created to satisfy the demand for more IP addresses as the internet continues to grow. It’s a 128-bit address scheme that allows for 340 undecillion (or 3.4×1038) IP addresses—that should tide us over for a bit.
Both IPV4 and IPV6 are still widely used, but the internet is slowly transitioning over to IPV6.
Sources
- Ben Gilbert, Engaget, “The United States Congress edits Wikipedia constantly,” July 11, 2014. Accessed February 25, 2021.
Author - Kevin Parrish
Kevin Parrish has more than a decade of experience working as a writer, editor, and product tester. He began writing about computer hardware and soon branched out to other devices and services such as networking equipment, phones and tablets, game consoles, and other internet-connected devices. His work has appeared in Tom’s Hardware, Tom's Guide, Maximum PC, Digital Trends, Android Authority, How-To Geek, Lifewire, and others. At HighSpeedInternet.com, he focuses on network equipment testing and review.
Editor - Aaron Gates







